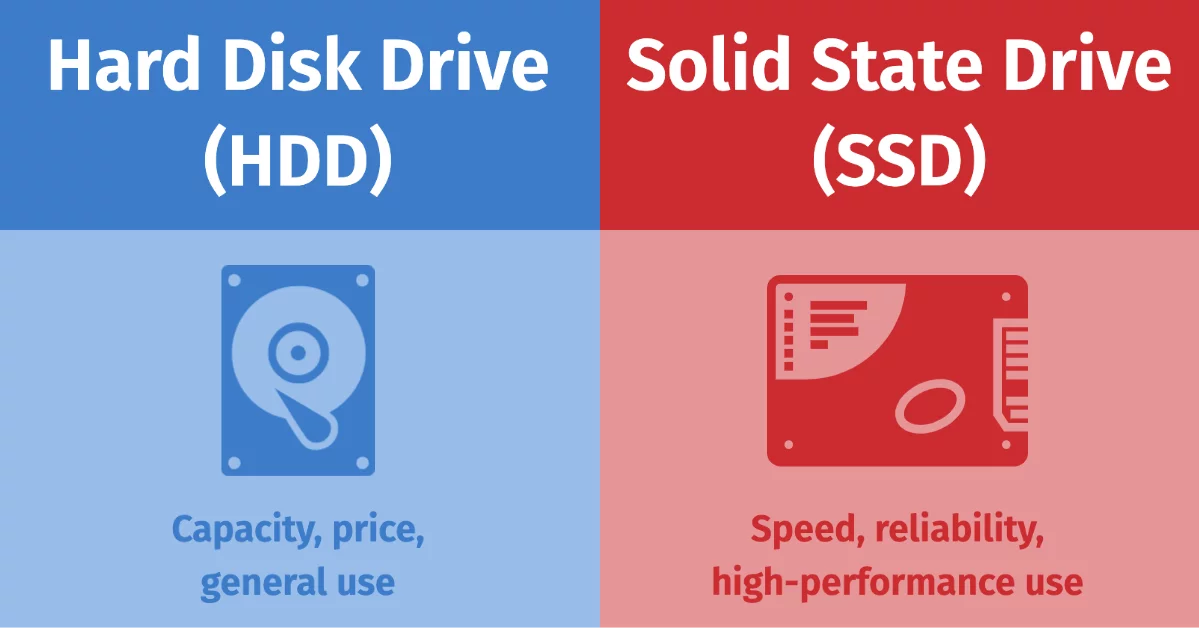
In the ever-evolving world of data storage, the choice between Hard Disk Drives and Solid-State Drives remains a crucial consideration for individuals and businesses alike. These two storage technologies differ significantly in structure, performance, and longevity, making it essential to understand their distinct advantages and limitations. HDDs, known for their affordability and high storage capacities, have long been the industry standard, while SSDs, with their superior speed and durability, are rapidly becoming the preferred choice for modern computing.
The decision between the two depends on various factors, including budget constraints, usage scenarios, and performance expectations. Whether you need vast storage for archiving large files or lightning-fast responsiveness for high-performance applications, selecting the right storage device can drastically impact your computing experience. Additionally, energy efficiency, noise levels, and long-term reliability further differentiate these storage solutions, influencing their suitability for different environments. With technology advancing at a rapid pace, understanding these nuances is more important than ever. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the key differences, advantages, and drawbacks of each option, helping you make an informed decision. By evaluating storage needs based on speed, durability, and cost-effectiveness, you can determine which solution best aligns with your specific requirements.
Understanding the Basics
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs):
Introduced in the 1950s, HDDs have been the cornerstone of data storage for decades. They operate using mechanical components, a spinning platter coated with magnetic material and a read/write head that moves to access data. This electromechanical system allows for the storage and retrieval of large amounts of data at a relatively low cost.
Solid State Drives (SSDs):
Emerging in the late 20th century, SSDs utilize flash memory to store data, eliminating the need for moving parts. This fundamental difference in architecture results in faster data access and improved durability. SSDs have rapidly gained popularity, especially in applications requiring high-speed data processing and reliability.
 Performance and Speed
Performance and Speed
One of the most significant distinctions between HDDs and SSDs lies in their performance metrics.
Speed: SSDs outperform HDDs in both read and write operations. Typical HDDs achieve read/write speeds up to 200 MBps, whereas SSDs can reach speeds exceeding 500 MBps, with some high-end models surpassing 3,000 MBps.
This substantial difference translates to faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and enhanced overall system responsiveness.
Latency: The absence of mechanical components in SSDs results in lower latency compared to HDDs. This means data retrieval is almost instantaneous, providing a smoother user experience, particularly in applications requiring rapid data access.
Nice To Read: Best-Selling Laptops in South Africa: Which One is Right for You
Durability and Reliability
The structural design of storage devices significantly impacts their durability.
HDDs:
The mechanical nature of HDDs makes them susceptible to physical shocks and wear over time. The moving parts can fail due to drops, vibrations, or general mechanical fatigue, leading to potential data loss.
SSDs:
In contrast, SSDs are more robust due to their lack of moving parts. This intrinsic durability makes them less prone to physical damage, offering greater reliability, especially in mobile devices or environments subject to movement.
 Storage Capacity and Cost Efficiency
Storage Capacity and Cost Efficiency
When evaluating storage solutions, capacity and cost are critical factors.
Capacity: Historically, HDDs have offered higher storage capacities at more affordable prices. However, advancements in SSD technology have led to increased capacities, with some models now exceeding 60 TB.
Despite this progress, high-capacity SSDs remain more expensive than their HDD counterparts.
Cost: The cost per terabyte is generally lower for HDDs, making them a cost-effective solution for bulk storage needs. For instance, enterprise-grade HDDs can cost more per TB, whereas SSDs may cost less per TB.
This price disparity is a crucial consideration for budget-conscious consumers and businesses.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Energy consumption is an increasingly important consideration in storage solutions.
HDDs:
The mechanical operations in HDDs require more power, leading to higher energy consumption and heat generation. This not only affects electricity costs but also necessitates additional cooling mechanisms, impacting the overall environmental footprint.
SSDs:
SSDs are more energy-efficient, consuming less power due to their non-mechanical design. This efficiency results in longer battery life for portable devices and reduced heat production, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly technology infrastructure.
 Form Factor and Noise Levels
Form Factor and Noise Levels
The physical characteristics of storage devices influence their suitability for various applications.
Size and Weight: SSDs are more compact and lightweight compared to HDDs, making them ideal for ultrabooks, tablets, and other portable devices where space and weight are critical considerations.
Noise: The operation of HDDs involves moving parts, which can generate audible noise and vibrations during use. SSDs operate silently, enhancing the user experience, especially in quiet environments or for users sensitive to noise.
Lifespan and Data Integrity
The longevity and reliability of data storage are paramount for both personal and professional use.
HDDs:
While susceptible to mechanical failures, HDDs do not have a finite number of write cycles, allowing for extensive read/write operations without degradation over time.
SSDs:
SSDs have a limited number of write cycles due to the nature of flash memory. However, modern SSDs employ technologies such as wear leveling and overprovisioning to mitigate this limitation, extending their usable life and ensuring data integrity.
Also Nice To Read: Why AMD Ryzen Laptops Are Gaining Popularity in South Africa
Use Cases and Recommendations
Choosing between an HDD and an SSD depends on specific use cases and priorities.
HDDs:
Ideal for scenarios requiring large storage capacities at a lower cost, such as archival storage, media libraries, and backup solutions. Their cost-effectiveness makes them suitable for bulk data storage where speed is not a critical factor.
SSDs:
Best suited for applications demanding high performance, quick data access, and reliability, such as operating systems, gaming, video editing, and mobile devices. Their speed and durability enhance productivity and user experience in environments where performance is paramount.
Choosing between an HDD and an SSD ultimately depends on your priorities whether it's affordability, speed, or durability. While HDDs remain a cost-effective solution for bulk storage, SSDs offer unparalleled performance, efficiency, and reliability. Upgrading to an SSD can transform your computing experience, enhancing speed and productivity. Invest in cutting-edge storage technology today with Tsele le Tsele Tech, your trusted source for premium Solid State Drives in South Africa!






